Key Takeaways
- Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the ovaries and are usually harmless, resolving on their own.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age, characterized by multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
- Common symptoms of PCOS include irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain.
- Unlike typical ovarian cysts, PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can lead to long-term health issues like diabetes and heart disease.
- Management of PCOS often involves lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes surgery to address symptoms and improve quality of life.
Introduction to Ovarian Cysts and PCOS
When it comes to women’s reproductive health, ovarian cysts and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are terms that often crop up in conversations. These conditions can cause confusion, as they share some similarities but are distinctly different. Understanding the nature of these conditions is crucial for managing them effectively and empowering women’s health education.
Overview of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on or within an ovary. Most ovarian cysts are benign and harmless, often resolving without treatment. They are quite common and can occur during the menstrual cycle. The majority of women will have an ovarian cyst at some point in their lives, but many will never even know it, as cysts often do not cause symptoms.
Introduction to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
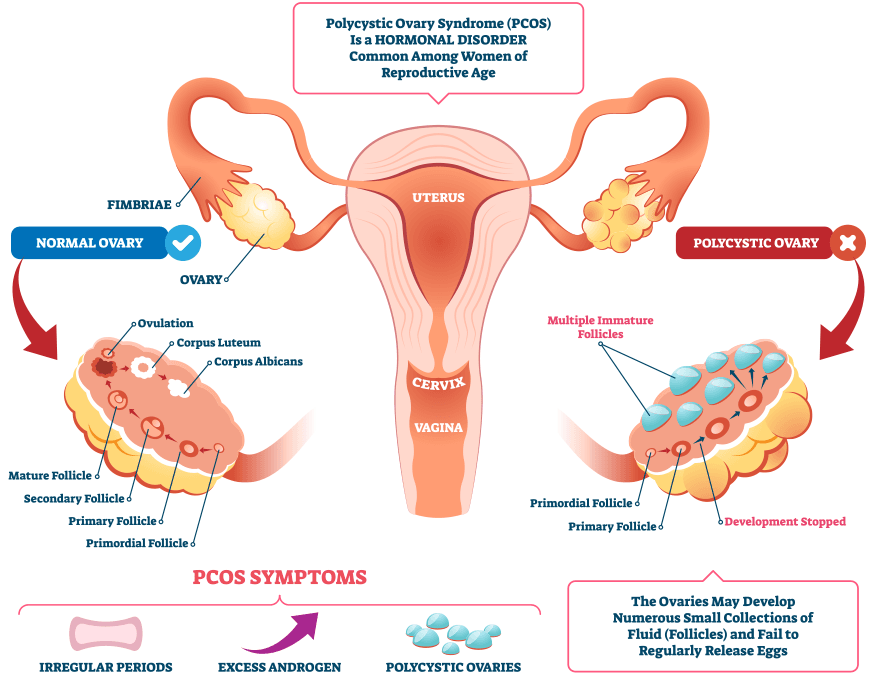
PCOS is a more complex condition, involving a range of symptoms and hormonal imbalances. It is a common endocrine disorder affecting women of reproductive age, characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual cycles, and elevated levels of male hormones (androgens). These hormonal imbalances can lead to a variety of symptoms and health complications.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
One common misconception is that all women with ovarian cysts have PCOS. This is not true. While PCOS involves multiple cysts, not all cysts indicate PCOS. Another misunderstanding is that PCOS only affects fertility. While infertility is a significant concern, PCOS can impact various aspects of health, including fertility concerns, metabolic and cardiovascular health.
“While ovarian cysts and PCOS can have similar symptoms in some cases, they are two very different conditions. Women can have multiple ovarian cysts and not suffer from PCOS; however, multiple ovarian cysts are also a symptom of PCOS.”
“What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS …” from www.renown.org and used with no modifications.
Characteristics of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can vary greatly in size and type, and while most are benign, they can occasionally cause discomfort or complications.
Definition and Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are typically classified into two main categories: functional cysts and pathological cysts. Functional cysts are the most common and occur as part of the normal menstrual cycle. They include follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts. Pathological cysts, on the other hand, may be benign or malignant and include dermoid cysts and cystadenomas.
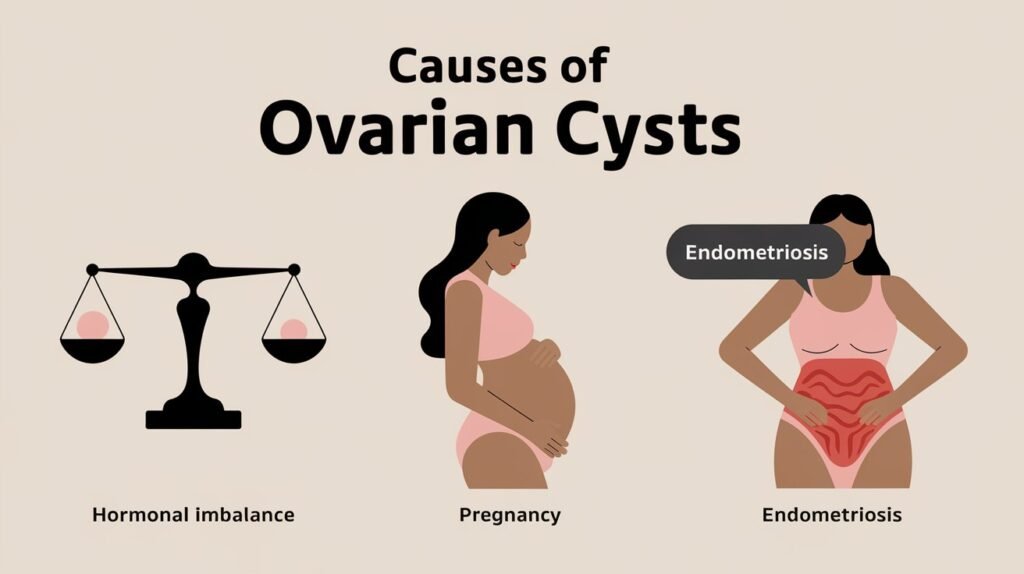
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of ovarian cysts is often linked to hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle. Factors that may increase the risk of developing cysts include hormonal problems, endometriosis, pregnancy, and severe pelvic infections. Most importantly, understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and management.
“Endometriosis can cause cysts called endometriomas. These cysts can be painful and require medical attention.”
Besides that, lifestyle factors such as diet and stress levels can also influence the likelihood of developing cysts, highlighting the importance of a balanced lifestyle.

Symptoms to Watch For
While many ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms, some may lead to pelvic pain, bloating, or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. If a cyst ruptures, it can cause sudden and severe pain, requiring immediate medical attention. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor any changes or developments.
Treatment Options
Treatment for ovarian cysts often depends on the size and type of the cyst, as well as the symptoms experienced. For many, watchful waiting is recommended, with follow-up ultrasounds to ensure the cyst resolves. In cases where cysts are large, persistent, or cause significant discomfort, surgical intervention may be necessary. Additionally, hormonal contraceptives may be prescribed to prevent the formation of new cysts.
Features of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a complex condition with a range of symptoms and potential health implications, affecting women differently.

Symptoms and Diagnosis of PCOS
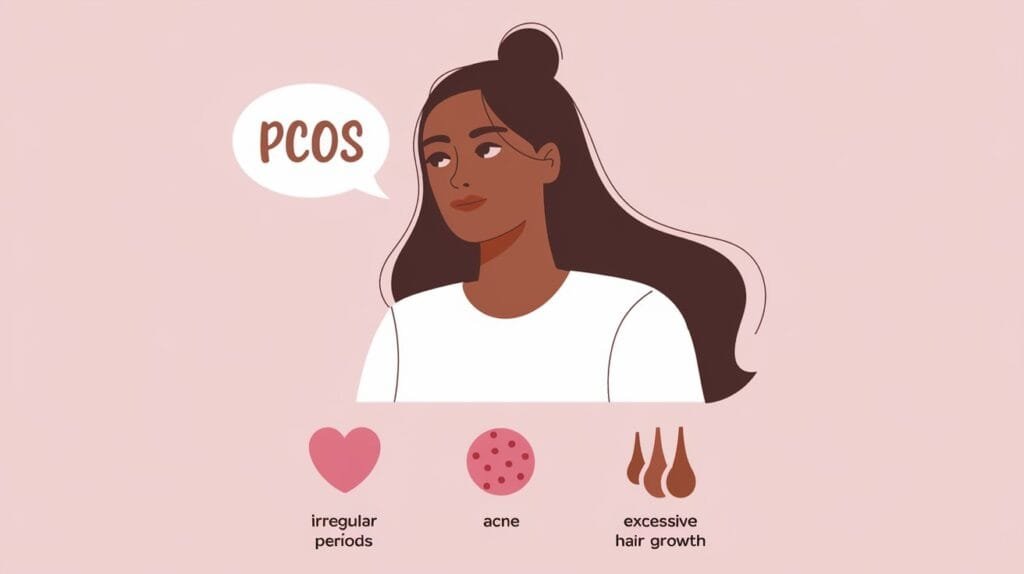
PCOS manifests through a variety of symptoms that can vary widely from person to person. Common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, which can mean having fewer periods or none at all. Women with PCOS may also experience excessive hair growth on the face and body, a condition known as hirsutism, as well as severe acne and thinning hair on the scalp.
Diagnosis of PCOS typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests to measure hormone levels, and ultrasound imaging of the ovaries. The presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, elevated levels of male hormones, and irregular menstrual cycles are key indicators used by healthcare providers to diagnose PCOS.
Impact on Health and Lifestyle
Living with PCOS can affect various aspects of a woman’s life. Besides the physical symptoms, many women experience emotional and psychological challenges, including depression and anxiety. The condition can also affect self-esteem and body image due to symptoms like weight gain and acne. For more information on the symptoms and causes of PCOS, visit this detailed resource.
Additionally, managing PCOS often requires lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine. These changes can help manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for women with PCOS, as many experience insulin resistance.
Long-Term Health Risks
PCOS is associated with several long-term health risks. Women with PCOS have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Furthermore, the hormonal imbalances in PCOS can lead to infertility and complications during pregnancy, such as gestational diabetes and pre-eclampsia.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Managing PCOS often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. A balanced diet and regular exercise are fundamental in managing weight and reducing insulin resistance. In some cases, medications such as metformin are prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.
Hormonal contraceptives can regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptoms like acne and excessive hair growth but do not address the root issues caused by PCOS. For those struggling with infertility, fertility treatments, including medications to induce ovulation, may be recommended. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan.
Distinguishing Between Ovarian Cysts and PCOS
Understanding the differences between ovarian cysts and PCOS is crucial for effective management and treatment. While both conditions involve the ovaries, their causes, symptoms, and implications are different.
Key Differences
Ovarian cysts are typically singular fluid-filled sacs that can form for various reasons and often resolve on their own. In contrast, PCOS is a hormonal disorder characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, along with other symptoms like irregular periods and elevated androgen levels. For a deeper understanding of this condition, check out what PCOS is.
Moreover, while ovarian cysts are often asymptomatic, PCOS involves a range of symptoms affecting both physical and hormonal health. It’s important to note that having ovarian cysts does not necessarily mean one has PCOS, as PCOS involves a broader set of criteria.

Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnosing ovarian cysts usually involves a pelvic exam and ultrasound imaging to assess the cyst’s size and type. Blood tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions. On the other hand, diagnosing PCOS requires a more comprehensive approach, including evaluating symptoms, hormone levels, and ovarian appearance.
Most importantly, a healthcare provider may use the Rotterdam criteria, which consider the presence of at least two of the following: irregular periods, high androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries visible on an ultrasound. This comprehensive diagnostic approach helps differentiate between PCOS and other conditions.
Hormonal Influence and Health Implications
The hormonal imbalances in PCOS play a significant role in its symptoms and associated health risks. Understanding these hormonal influences is key to managing the condition effectively. For a deeper dive into PCOS symptoms and management, explore more resources.
Androgens and PCOS
Androgens, often referred to as male hormones, are present in both men and women. In women with PCOS, androgen levels are higher than normal, leading to symptoms such as excessive hair growth, acne, and scalp hair thinning. These symptoms can be distressing and impact a woman’s quality of life.
Insulin Resistance Connection
Insulin resistance is a common feature of PCOS, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Managing insulin resistance is crucial for women with PCOS, as it can help alleviate symptoms and reduce long-term health risks.
Besides that, lifestyle changes such as a low-sugar diet and regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help manage PCOS symptoms. Medications like metformin may also be prescribed to support insulin regulation.
Fertility and Reproductive Health Challenges
PCOS can significantly impact fertility and reproductive health. Irregular menstrual cycles can make it challenging to predict ovulation, complicating efforts to conceive. Women with PCOS may also experience anovulation, where the ovaries do not release an egg during a menstrual cycle.
Despite these challenges, many women with PCOS can conceive with the help of fertility treatments. Medications like clomiphene citrate can stimulate ovulation, increasing the chances of pregnancy. It’s important to consult with a fertility specialist to explore the best options for individual circumstances.
Lifestyle Modifications and Natural Remedies
Managing PCOS and ovarian cysts often involves making lifestyle modifications that can significantly improve symptoms and overall health. While medical treatments are essential, integrating natural remedies and lifestyle changes can provide additional benefits and help manage the condition effectively.
Diet and Nutrition Tips
Diet plays a crucial role in managing PCOS. A balanced diet rich in whole foods can help regulate hormones and improve insulin sensitivity. Focus on incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. It’s also beneficial to limit processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats.
Consider adopting a low-glycemic index diet, which can help manage insulin levels and reduce symptoms. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, legumes, and most fruits and vegetables, release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.

Exercise and Weight Management
Regular physical activity is essential for managing PCOS and maintaining a healthy weight. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, reduce stress, and promote overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, each week.
“Exercise not only aids in weight management but also improves mood and energy levels, which are vital for managing PCOS.”
Strength training exercises, such as weight lifting or resistance band workouts, can also be beneficial. Building muscle mass helps increase metabolism and burn more calories, even at rest. For more information on managing PCOS, you can explore the symptoms and causes of PCOS.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to lifestyle changes, some women find relief from PCOS symptoms through alternative therapies. While these should not replace medical treatments, they can complement conventional approaches.
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help regulate menstrual cycles and improve ovulation in women with PCOS.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, like spearmint tea and cinnamon, are believed to help reduce androgen levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any herbal supplements.
- Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: Practices such as yoga and meditation can help reduce stress levels, which can exacerbate PCOS symptoms.
It’s important to discuss any alternative therapies with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific situation.
Future Perspectives and Research Developments
Ongoing research continues to shed light on PCOS and ovarian cysts, offering hope for new treatments and a better understanding of these conditions. Advances in medical science and technology promise potential breakthroughs that could transform how these conditions are managed.
Ongoing Research in PCOS
Current research efforts are focused on understanding the underlying causes of PCOS and identifying new treatment targets. Studies are exploring the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the development of PCOS, which could lead to more personalized treatment approaches.
Researchers are also investigating the role of gut microbiota in PCOS, as emerging evidence suggests a connection between gut health and hormonal balance. This line of research could open new avenues for treatment through dietary and probiotic interventions.

Innovations in Treatment and Diagnosis
Innovations in medical technology are enhancing the diagnosis and treatment of PCOS. Advanced imaging techniques and biomarkers are being developed to improve diagnostic accuracy and monitor treatment progress.
In terms of treatment, new medications and therapies are being tested to address the hormonal and metabolic aspects of PCOS more effectively. These innovations aim to provide more targeted and effective solutions for managing the condition.
Potential Breakthroughs
The future holds promising potential for breakthroughs in PCOS management. Gene therapy and personalized medicine approaches are on the horizon, offering the possibility of tailored treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
Moreover, ongoing research into the long-term health risks associated with PCOS is helping to develop strategies for prevention and early intervention, ultimately improving the quality of life for women affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Understanding PCOS and ovarian cysts can be challenging, but having the right information can empower you to take control of your health. Here are some common questions and answers to help clarify these conditions.
- What are the main symptoms of ovarian cysts?
- Ovarian cysts often do not cause symptoms and may go unnoticed. However, when symptoms occur, they can include pelvic pain, bloating, and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. If a cyst ruptures, it can cause sudden and severe pain, requiring immediate medical attention.
- What distinguishes ovarian cysts from PCOS?
- Ovarian cysts are usually single, fluid-filled sacs that may form on an ovary and typically resolve on their own. PCOS, however, is a hormonal condition that includes multiple small cysts on the ovaries, along with symptoms like irregular periods and elevated androgen levels, affecting various aspects of health.
- How is PCOS diagnosed?
- Diagnosis of PCOS involves a review of symptoms, hormone level testing, and ultrasound imaging of the ovaries. The Rotterdam criteria are often used, requiring at least two of the following for diagnosis: irregular menstrual cycles, high androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries visible on ultrasound.
- Can ovarian cysts turn into cancer?
- While most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous), some types, especially if persistent or complex, may require monitoring. A healthcare provider can assess the risk and suggest appropriate follow-up care.
- How can lifestyle changes help manage PCOS?
- Diet and exercise can significantly help manage symptoms of PCOS, especially for those with insulin resistance. A balanced diet rich in whole foods, combined with regular physical activity, can improve insulin sensitivity and manage weight, which is beneficial for overall symptom relief.
- Is pregnancy possible with PCOS?
- Yes, many women with PCOS can conceive, though they may face challenges due to irregular ovulation. Fertility treatments, such as medications to stimulate ovulation, are available, and a fertility specialist can provide guidance on the best options.
- Are there natural remedies to help manage PCOS symptoms?
- While medical treatments are often necessary, some natural remedies like dietary changes, herbal supplements (e.g., cinnamon, spearmint tea), and stress-reducing practices like yoga and mindfulness can complement conventional treatments. It’s best to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
- What are the long-term health risks associated with PCOS?
- PCOS increases the risk of long-term health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and certain pregnancy complications. Managing PCOS through lifestyle and medical treatment can reduce these risks.
- Can ovarian cysts recur?
- Yes, ovarian cysts can recur, especially functional cysts that form during the menstrual cycle. Hormonal contraceptives may help reduce the risk of new cyst formation.
- What should I do if I experience severe pain from a cyst?
- If a cyst ruptures or causes sudden, intense pain, seek immediate medical attention, as this may require urgent care to prevent complications.
In contrast, PCOS symptoms are more varied and include irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain. These symptoms are due to hormonal imbalances and require a different approach to management. For more details on these symptoms, you can explore PCOS symptoms and management strategies.