Introduction to PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common health condition affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterized by hormonal imbalances and metabolism issues, leading to a variety of signs and symptoms. Understanding these signs is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a condition where the ovaries produce an abnormal amount of androgens, male sex hormones that are usually present in women in small quantities. It can lead to the development of cysts (small fluid-filled sacs) in the ovaries.
Signs and Symptoms of PCOS
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
- Infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles are common in PCOS.
- Periods may come every few months or not at all.
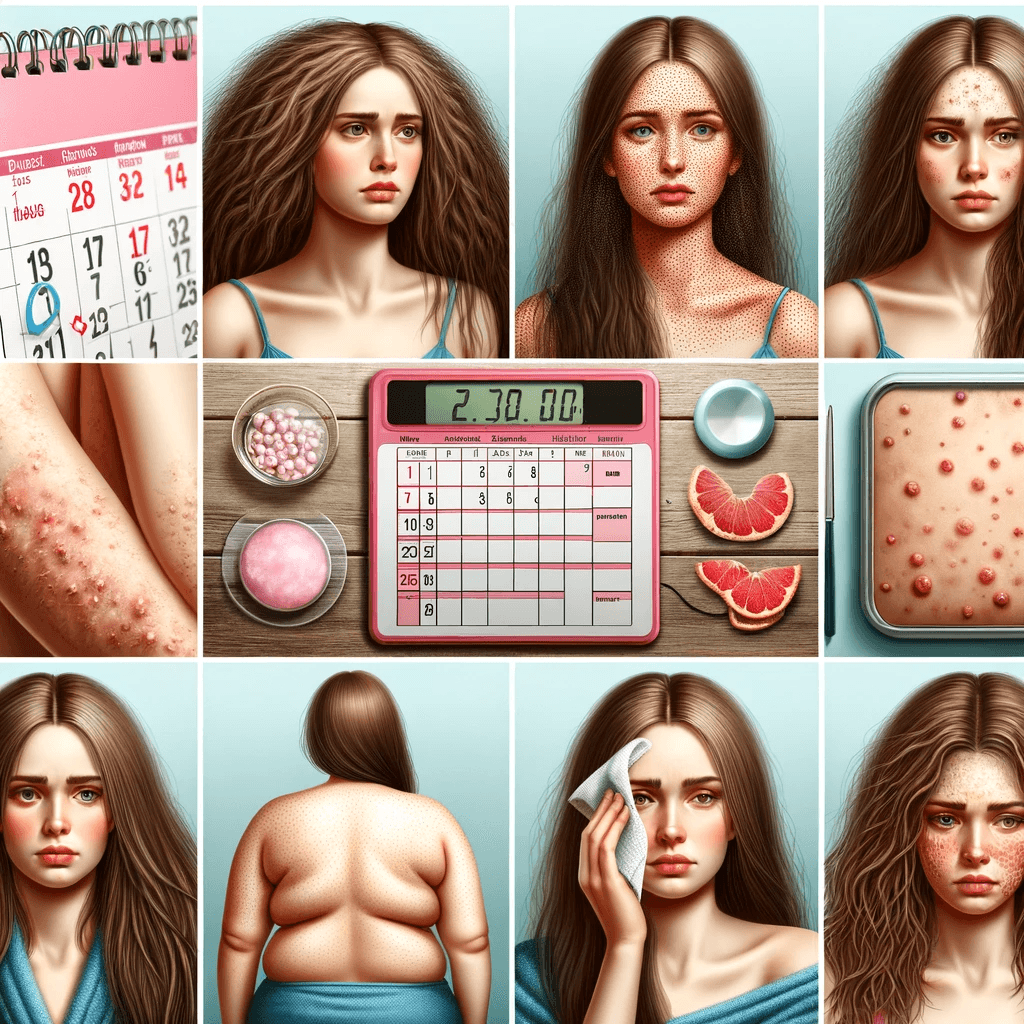
2. Heavy Bleeding
- When women with PCOS get their period, they might experience heavier bleeding than usual.
3. Hair Growth
- More than 70% of women with this condition experience hirsutism — excessive hair growth on the face, chest, back, or buttocks.
4. Acne
- Hormonal changes can lead to acne on the face, chest, and upper back.
5. Weight Gain
- Up to 80% of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
- Difficulty losing weight is common.
6. Male-pattern Baldness
- Hair on the scalp gets thinner and may fall out.
7. Darkening of the Skin
- Dark patches of skin can form in body creases like those on the neck, in the groin, and under the breasts.
8. Headaches
- Hormone changes can trigger headaches in some women.
Causes of PCOS
Genetic Factors
- PCOS often runs in families, suggesting a genetic link.

Insulin Resistance
- Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, leading to increased blood sugar levels and higher production of androgens.
Inflammation
- Women with PCOS often have increased levels of inflammation in their body.
Complications of PCOS
Infertility
- PCOS is one of the leading causes of infertility in women.
Metabolic Syndrome
- Includes conditions like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
Sleep Apnea
- It is more common in overweight women, including those with PCOS.
Depression and Anxiety
- Hormonal changes and symptoms like unwanted hair growth can negatively impact mental health.
Endometrial Cancer
- Irregular periods can lead to endometrial cancer.
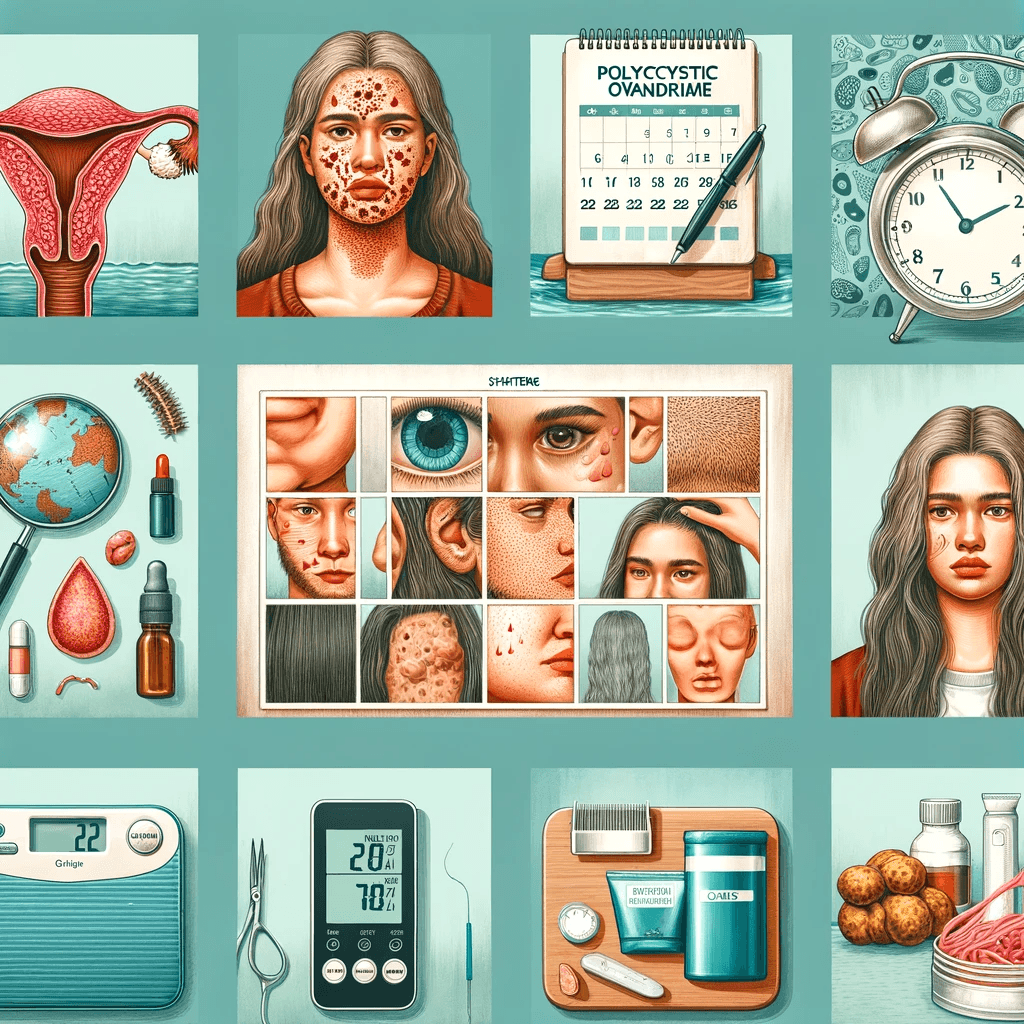
Diagnosis of PCOS
- Medical History: A doctor will discuss your menstrual cycles, weight changes, and other symptoms.
- Physical Exam: Includes checking for signs of excess hair growth, insulin resistance, and acne.
- Blood Tests: Measure hormone levels to rule out other possible conditions.
- Ultrasound: Checks the appearance of your ovaries and the thickness of the lining of your uterus.
Treatment and Management of PCOS
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet and exercise are important for managing PCOS.
- A healthy diet can help regulate your menstrual cycle and lower your blood sugar levels.
Medication
- Birth control pills to regulate menstrual cycles.
- Metformin to improve insulin resistance.
- Hair removal medicines.
Fertility Treatments
- Medications to help women ovulate.
Conclusion
PCOS is a complex condition with a variety of symptoms and potential complications. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term complications. If you suspect you have symptoms of PCOS, it’s important to seek medical advice for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Further Reading and Resources
For more detailed information on PCOS, visit reputable health websites such as:

